|
I am a fresh Ph.D. graduate from National Taiwan University under the supervision of Prof. Shao-Hua Sun. I completed my bachelor's degree in Electronic Engineering at NTU. During my Ph.D., I previously worked in the Vision and Learning Lab at NTU and collaborated with Chunghwa Telecom Laboratories. I also worked with Inventec AI Center during my internship. Email / CV / Google Scholar / Github |

|
|
I'm interested in reinforcement learning, computer vision, and machine learning. My research is about utilizing machine learning techniques to solve application problems, including multi-label classification, anomaly detection, and imitation learning. |
|
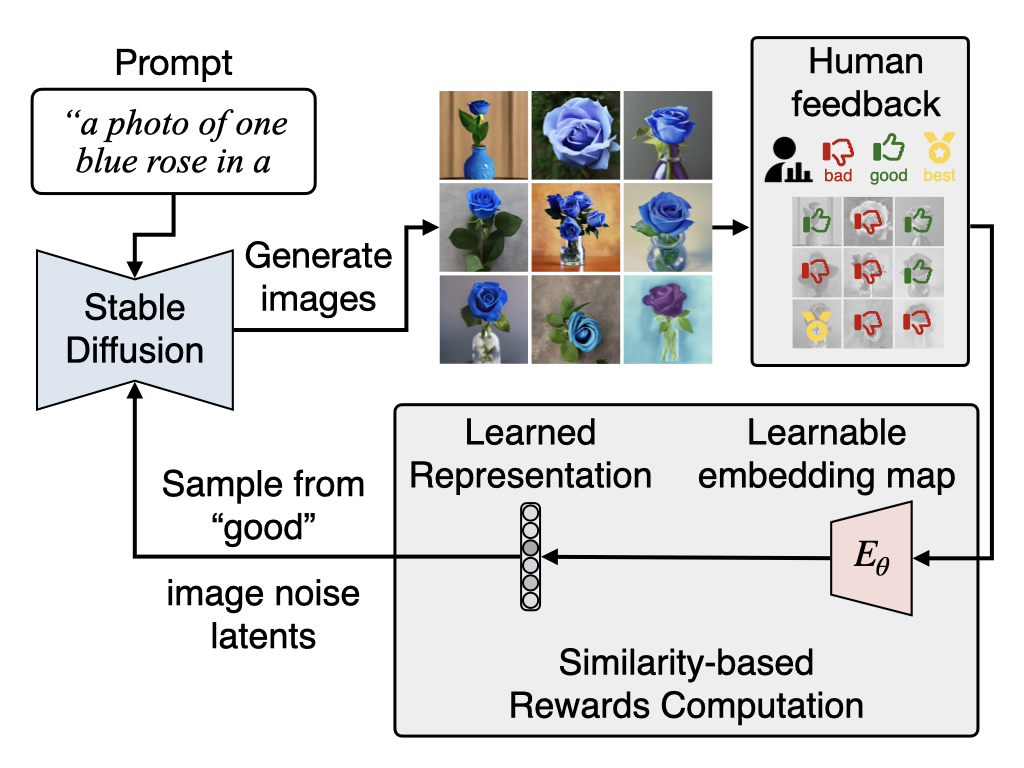
Ayano Hiranaka*,Shang-Fu Chen*, Chieh-Hsin Lai*, Dongjun Kim, Naoki Murata, Takashi Shibuya, Wei-Hsiang Liao, Shao-Hua Sun†, Yuki Mitsufuji† International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) , 2025 Project Page / Paper To effectively and efficiently utilize human feedback, we develop a framework, HERO, which leverages online human feedback collected on the fly during model learning. Specifically, HERO features two key mechanisms: (1) an online training method that captures human feedback and provides informative learning signals for fine-tuning, and (2) generating images from SD's refined initialization samples, enabling faster convergence towards the evaluator's intent. |
|
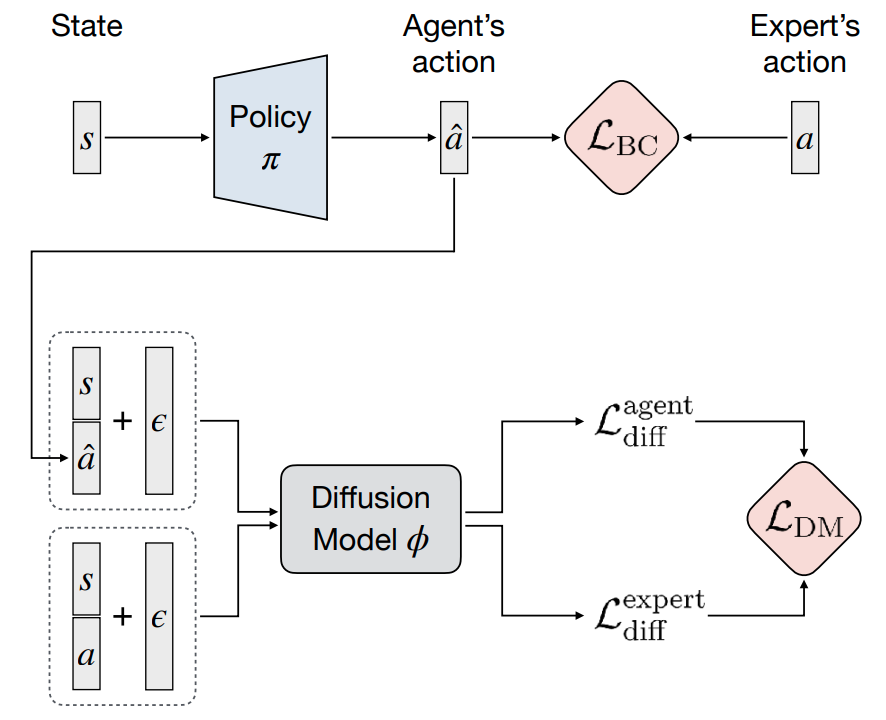
Shang-Fu Chen*, Hsiang-Chun Wang*, Ming-Hao Hsu, Chun-Mao Lai, Shao-Hua Sun, International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2024 Project Page / Paper / Poster This work aims to augment BC by employing diffusion models for modeling expert behaviors and designing a learning objective that leverages learned diffusion models to guide policy learning. To this end, we propose an imitation learning framework that benefits from modeling both the conditional and joint probability of the expert distribution. Our proposed diffusion model-augmented behavioral cloning (DBC) employs a diffusion model trained to model expert behaviors and learns a policy to optimize both the BC loss (conditional) and our proposed diffusion model loss (joint). Our proposed method outperforms baselines or achieves competitive performance in various continuous control domains, including navigation, robot arm manipulation, dexterous manipulation, and locomotion. |
|
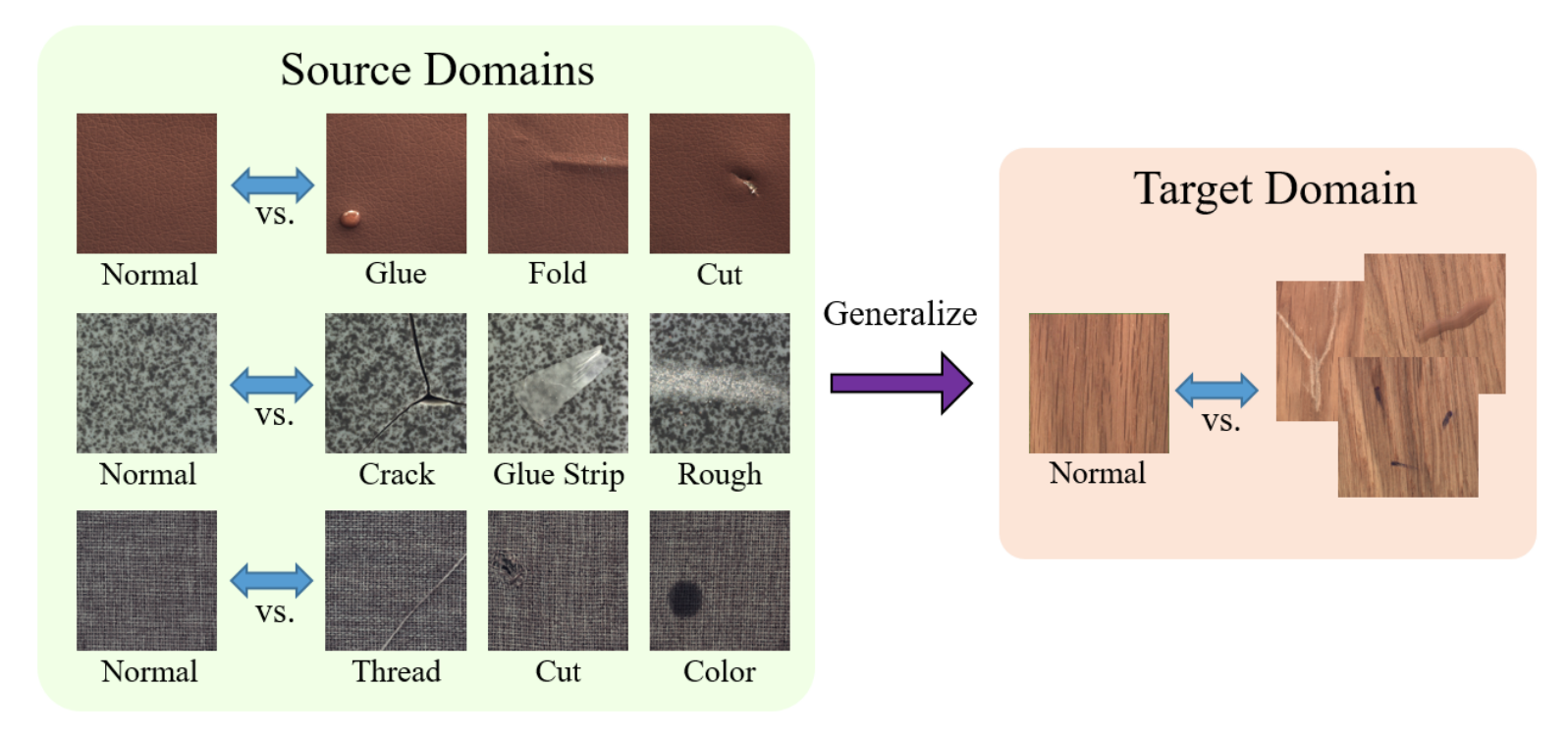
Shang-Fu Chen, Yu-Min Liu, Chia-Ching Lin, Trista Pei-Chun Chen, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), 2022 Paper In this paper, we address the task of domain-generalized textured surface anomaly detection. We propose a patch-based meta-learning model that exhibits promising generalization ability. By observing normal and abnormal surface data across multiple source domains, our model can generalize to an unseen textured surface of interest and localize abnormal regions in the query images. Our experiments verify that our model performs favorably against state-of-the-art anomaly detection and domain generalization approaches in various settings. |

|
Zih-Ching Chen*, Lin-Hsi Tsao*, Chin-Lun Fu*, Shang-Fu Chen, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), 2022 Paper This work aims to apply domain generalization and feature disentanglement for the face anti-spoofing (FAS) problem, which aims at distinguishing face spoof attacks from authentic ones. We propose a learning frame to disentangle facial liveness representation from the irrelevant ones (i.e., facial content and image domain features). The resulting liveness representation exhibits sufficient domain invariant properties and thus can be applied for performing domain-generalized FAS. Our experiments verify that our model performs favorably against state-of-the-art approaches on five benchmark datasets with various settings. |
|
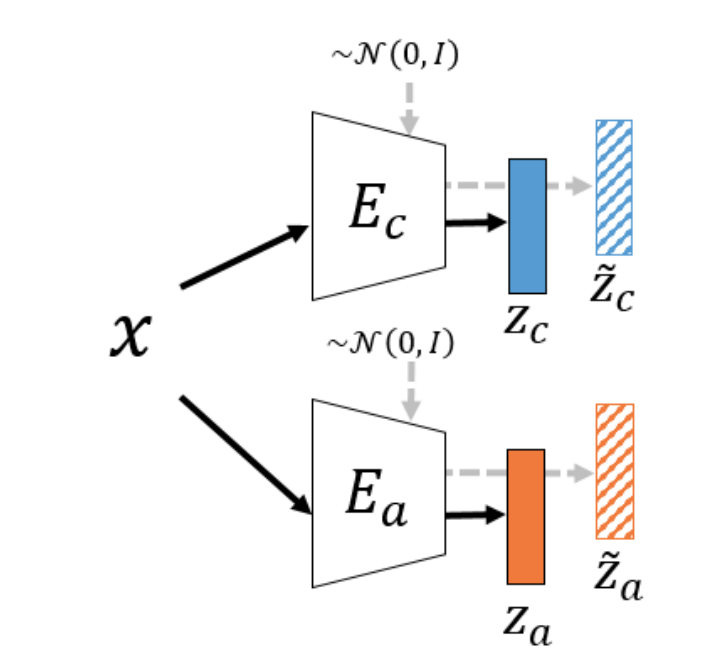
Shang-Fu Chen, Jia-Wei Yan, Ya-Fan Su, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2021 Paper This work aims to apply feature disentanglement on existing/trained generative models. To this end, we propose a decomposition-GAN (dec-GAN), which can decompose an existing latent representation into content and attribute features. Guided by the classifier pre-trained on the attributes of interest, our dec-GAN decomposes the attributes of interest from the latent representation, while data recovery and feature consistency objectives enforce the learning of our proposed method. Our experiments on multiple image datasets confirm the effectiveness and robustness of our dec-GAN over recent representation disentanglement models. |

|
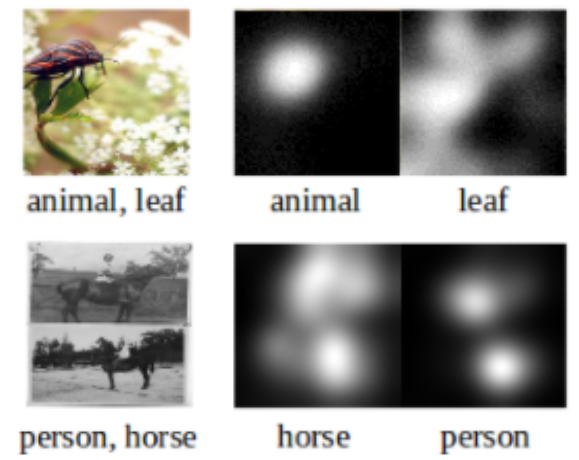
Shang-Fu Chen*, Yi-Chen Chen*, Chih-Kuan Yeh, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2018 Paper We propose a recurrent neural network (RNN) based model for image multi-label classification. Our model integrates the learning of visual attention and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) layers. The LSTM module learns the labels of interest and their co-occurrences, while the attention module captures the associated image regions. Unlike existing approaches, training our model does not require pre-defined label orders. We introduce a robust inference process to address the prediction error propagation problem. Our experiments on NUS-WISE and MS-COCO datasets confirm the design of our network and its effectiveness in solving multi-label classification problems. |